
However, the problem is that even a legitimate model can be flagged, depending on the network’s response. As a result, strange looking anomalies are flagged. As the database increases, the processing load increases and so the system takes time to analyse each connection and verify it.Īnomaly based IDS: This uses machine learning to detect intrusions by comparing trustworthy models with new models. But it is very easy to bypass it by making tiny changes to the code. Signature-based IDS is only as good as how up-to-date its database is at that given moment. Signature based IDS: This focuses on searching for ‘signature’ patterns, or an identity of an intrusion, or a specific intrusion event. It looks at the entire system’s file set and compares it to previous logs of the file set. It works as a second line of defence against malicious data if NIDS fails to detect something. So, there are chances of it missing an attack or not detecting something in encrypted traffic.Ī host intrusion detection system (HIDS) is established on all devices in the network. NIDS analyses a large volume of network traffic, which means it has low specificity. They are relatively easy to secure and thus, an intruder may not realise that an attack is being detected. Network-based intrusion detection systems (NIDS) are deployed at strategic points throughout the network, basically to keep a watch over places where the traffic is most likely to be vulnerable. Traffic flooding: This is also known as DDoS attack.
SNORT FOR MAC SOFTWARE
Basically, as the word itself says, this software is designed to damage or disrupt the system. Malware: This includes worms, trojans, viruses and bots.
SNORT FOR MAC MAC
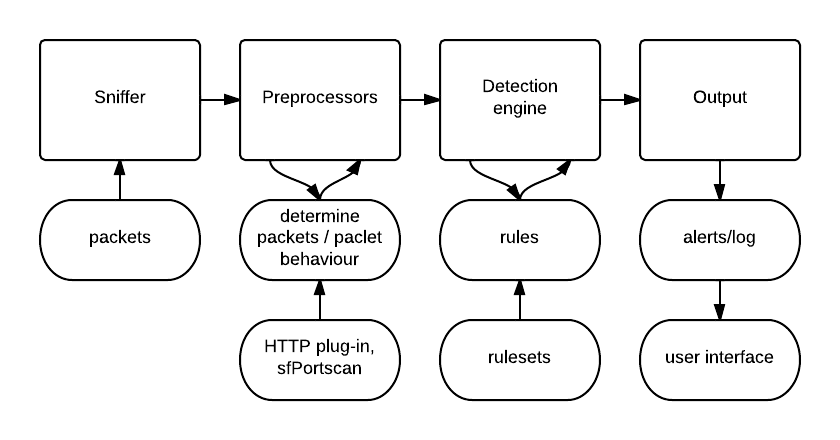
Scanning attack: This involves sending packets/information to a network in an attempt to gather data about the network, e.g., blind SQL injection. To detect and to prevent hackers and attackers from penetrating a system, we need to have a basic understanding of the attacks that can be possibly performed on it.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
